Question = Is vitamin e polar or nonpolar
Answer = vitamin e is Nonpolar

What is polar and non-polar?
Polar
"In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole ormultipole
Polar molecules must contain polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. A polar molecule with two or more polar bonds must have an asymmetric geometry so that the bond dipoles do not cancel each other.
Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points." (Wikipedia)
Polar molecules
A polar molecule has a net dipole as a result of the opposing charges (i.e.having
http://www.school-for-champions.com
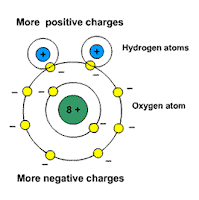
Picture: water is a polar molecule
Example polar molecules
Ammonia (NH3)
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
Nonpolar molecules
A molecule may be nonpolar either when there is an equal sharing of electrons between the two atoms of a diatomic molecule or because of the symmetrical arrangement of polar bonds in a more complex molecule. (Wikipedia)
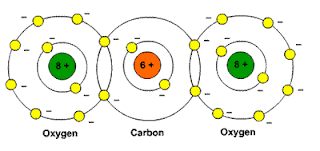
http://www.school-for-champions.com
Picture: Carbon dioxide
Example molecules non polar
Toluene
Gasoline
Helium (He)
Neon (Ne)
Krypton (Kr)
Xenon (Xe)
Hydrogen (H2)
Nitrogen (N2)
Oxygen (O2)
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Methane (CH4)
Ethylene (C2H4)
List molecules polar andnon polar
Molecules polar
SCN- (Thiocyanate)
HCO3- (Bicarbonate)
BrCl3 (Bromine Trichloride)
HCO3-1
AsCl3 (Trichloroarsine)
OCl2
NO2Cl (Nitryl chloride)
CH3F (Fluoromethane)
H3O+ Hydronium
ClF
ClF3 (Chlorine trifluoride)
CF2Cl2 (Dichlorodifluoromethane)
SeF4
CH3OCH3 (Dimethyl ether)
CH3CH2OH (Ethanol)
NH2-
BrF3 (BROMINE TRIFLUORIDE)
CH3NH2 (Methylamine)
CH2Br2 (Dibromomethane)
HI (Hydrogen iodide)
NH4NO3 (Ammonium nitrate)
IF5 (Hydrogen cyanide)
OH2 (Hydroxide)
C2Cl2
NO+ (nitrilooxonium
SBr2
ICl4+
NO
CH3OH (Methanol)
SCl6
NOBr
CH4O (Methanol)
ICl3 (Iodinetrichloride
BrF5 (BROMINE PENTAFLUORIDE)
PCl5 (PHOSPHORUS PENTACHLORIDE)
CH2F2 (Difluoromethane)
SeH2 (Hydrogenselenide
COS (Cobalt sulfide)
OF2 (Oxygendifluoride
H2SO4 (SULFURIC ACID)
H2CO (Formaldehyde)
NF3 (NITROGEN TRIFLUORIDE)
C2H2Br2 (Acetylenedibromide
TeF4
SCN
CLO3- (Chlorate)
ICl5
urea
SO2Cl2 (Sulfuryl chloride)
H2Se (Hydrogenselenide
NH2
XeO3
SbF3
CaCl2 (CALCIUM CHLORIDE)
AsF3 (ARSENIC TRIFLUORIDE)
C2H2 (Ethyne)
BrF
Cl2O
IF3 (Iodinetrifluoride
SH2
SCl4
CO (Carbon monoxide)
H3O
HNO3 (NITRIC ACID)
N2H2
NBr3
So3 2-
CH3COOH (acetic acid)
salt
SeO2
nitrogen
CCl2F2
N2H4
C2H5OH
NoCl
C2H6O (Ethanol-d6)
SOCl2
H3O+ (Hydronium)
CHF3 (Fluoroform)
HClO
NI3 (Nitrogen triiodide)
NaCl (sodium chloride)
AsH3 (Arsine)
NH2Cl
OCS (Carbonyl sulfide)
SiCl2F2
glucose
CH3
N2O
PoCl3 (PHOSPHORUS OXYCHLORIDE)
MgCl2
vinegar
IOF5
phosphate
CHBr3 (Bromoform)
ICl
carbon
sulfur
PBr3 (PHOSPHORUS TRIBROMIDE)
SF2 (Sulfurdifluoride
NH3 (ammonia)
SO2 (sulfur dioxide)
CH2Cl2 (DICHLOROMETHANE)
SF4
H2S (hydrogen sulfide)
CHCl3 (CHLOROFORM)
PCl3 (PHOSPHORUS TRICHLORIDE)
SCl2 (Sulfurdichloride
PH3 (Phosphine)
CH2O (Formaldehyde)
HF (HYDROFLUORIC ACID)
HBr
NCl3 (Nitrogentrichloride
PF3 (Phosphorustrifluoride
ethyl
NO3- (nitrate)
NO2 (Nitrogen dioxide)
H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide)
CH3Br (Bromomethane)
cn
O3 (OZONE)
CH3CL (Chloromethane)
ammonia
OH- (Hydroxide)
NO2- COCl2 (Cobalt(
glycerol
oh
chloroform
nitrogen trichloride
benzoic
ether
no3
CLF5 methylene chloride
sodium
CH3SH
Na2SO4
sodium
CaCO3
1-butanol
Clo
C4H10
libr
cabr2 (Calcium bromide)
CH3CN (ACETONITRILE)
CH3CH2CH2OH
C6H12O6
LiNO3 (Lithium nitrate)
MgO
SeOBr2
clo3
c3h7oh
nai
glycerine
bri5
BrO2
ammonium
CF3Cl
BF2Cl
IBr
GaCl3
KMnO4 (POTASSIUM PERMANGANATE)
Na2S (sodium sulfide)
KOH (POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE)
HCOOH
KBr
carbohydrates
ClO4
Cl2CO
clo2-
succinic
H2SO3 (Sulfurous acid)
sodium
ethyne
NO2F
CCL3F (Fluorotrichloromethane)
ammonium
ibr3
fluoromethane
C2H5Cl TeCl4
2-propanol
starch
ch2cl
XeOF4
SnCl2
SCO (Carbonyl sulfide)
SbBr3
H2CS
HC2H3O2
po ( oh) 3
Propanol
1-propanol
bro3-
ch3ch2ch2ch3
CF2Br2
acetic acid
aniline
CF
chlorine trifluoride
phenol
clo2
potassium permanganate
CH2S
nitrogen monoxide
ch3cho
glass
SH
COH2
SOF4
DNA
CH3CH2NH2
Malonic Acid
ethylene glycol
isopropyl alcohol
hydrogen bromide
SeCl4
hydrogen peroxide
ozone
c3h6o
formaldehyde
po3 3
difluoromethane
aspirin
CHCl2
rubbing alcohol
fluorene or fluorenol
vitamin c
HCl
nitrate
dimethyl ether
SCl
if4+
Molecules non polar
HBrO
SiF4 (Silicontetrafluoride
CH3CH3 (Ethane)
N2 (Nitrogen)
CO3 2- (Carbonate)
Heptane
XeO4 (Xenontetroxide
KNO3 (Potassium nitrate)
CH3I (Methyl iodide)
CBr4 (Carbontetrabromide
AlCl3 (Aluminumtrichloride
C6H6 (benzene)
NH4Br
C2H4Cl2 (dichloroethane
ligroin
SO4 2- (Sulfate)
C2H4
SF6 (Sulfur hexafluoride)
BH3 (Borane)
C2F2 (Ethyne)
C6H14 (HEXANE)
PO4 3- (phosphate)
GeH4 (Germane)
PBr5 (Phosphorus pentabromide)
NH4 (ammonium)
wax
CI4 (Tetraiodomethane)
bbr3 (BORON TRIBROMIDE)
H2 (Hydrogen)
IF4-
BeF2 (Berylliumdifluoride
I2 (Iodine)
GaH3 (Gallane)
SeBr4 (Seleniumtetrabromide
KrF4
SiBr4
C2H6 (Ethane)
O2 (Oxygen)
biphenyl
PO4 3
P4 (Phosphorustetramer
SO4 2-
naphthalene
XeCl2
BrCl5
SeF6
SeO3
SiH4 (silane
carbon tetrabromide
AsF5 (Arsenic pentafluoride)
BeH2 (Berylliumhydride
SiO2
KrF2
CH2
cholesterol
F2 (Fluorine)
pentane
ClF2
C3H8
Propane
cyclohexane
toluene
SiCl4 (Tetrachlorosilane)
chlorine
PF5 (Pentafluorophosphorane)
BrCl
CO2 (carbon dioxide)
CCl4 (CARBON TETRACHLORIDE)
XeF2
CS2 (CARBON DISULFIDE)
SO3 (SULFUR TRIOXIDE)
XeF4 (Xenontetrafluoride
BCl3 (BORON TRICHLORIDE)
BeCl2 (Berylliumdichloride
CF4 (CARBON TETRAFLUORIDE)
Cl2 (Chlorine)
Br2 (Bromine)
Hexane
carbon
i3-
carbon tetrachloride
carbon disulfide
methane
glycine
sulfur
benzophenone
oxygen
AlF3 (Aluminum fluoride)
beryllium dichloride
C8H18 (octane)
C2Cl4
PF6-
XeCl4
SbF5 (ANTIMONY PENTAFLUORIDE)
CH3CH2CH3
C5H12 (PENTANE)
silane
s8
BF4 BF4-
SeCl6
BeBr2
BeI2
CSe2
Pcl4
C3H6
AlH3 (Aluminumtrihydride
TeO3 (Telluriumtrioxide
Br -Br
AsCl5
octane
carbonate ions
ClF4 plus
acids
kerosene
acetylene
C-C
ethane
CCl
Cl4
cbr
sulfate
butter
triglycerides
grease
beryllium chloride
carbon tetrafluoride
butane
silicon tetrafluoride
nitrogen
ICl2-
bromine
hydrocarbon
HE
boron trichloride
CS
sulfur hexafluoride
sis2
xenon tetrafluoride
CH4
vitamin e
Ionic
NaBr
KCl
NaF
kf
NaNO3
cao
ki lif
licl
ammonium
MgF2
Resources:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemical_polarity
http://www.school-for-champions.com/chemistry/polar_molecules.htm#.WZIGddJJbcc
reference.com
www.quora.com
answers.yahoo.com
youtube.com
google.com
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
If the answer is wrong, pleasecomment in below article !
Answer = vitamin e is Nonpolar

What is polar and non-polar?
Polar
"In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole or
Polar molecules must contain polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. A polar molecule with two or more polar bonds must have an asymmetric geometry so that the bond dipoles do not cancel each other.
Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points." (Wikipedia)
Polar molecules
A polar molecule has a net dipole as a result of the opposing charges (i.e.
http://www.school-for-champions.com
Picture: water is a polar molecule
Example polar molecules
Ammonia (NH3)
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)
Nonpolar molecules
A molecule may be nonpolar either when there is an equal sharing of electrons between the two atoms of a diatomic molecule or because of the symmetrical arrangement of polar bonds in a more complex molecule. (Wikipedia)

http://www.school-for-champions.com
Picture: Carbon dioxide
Example molecules non polar
Toluene
Gasoline
Helium (He)
Neon (Ne)
Krypton (Kr)
Xenon (Xe)
Hydrogen (H2)
Nitrogen (N2)
Oxygen (O2)
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Methane (CH4)
Ethylene (C2H4)
List molecules polar and
Molecules polar
SCN- (Thiocyanate)
HCO3- (Bicarbonate)
BrCl3 (Bromine Trichloride)
HCO3-1
AsCl3 (Trichloroarsine)
OCl2
NO2Cl (Nitryl chloride)
CH3F (Fluoromethane)
H3O+ Hydronium
ClF3 (Chlorine trifluoride)
CF2Cl2 (Dichlorodifluoromethane)
SeF4
CH3OCH3 (Dimethyl ether)
CH3CH2OH (Ethanol)
NH2-
BrF3 (BROMINE TRIFLUORIDE)
CH3NH2 (Methylamine)
CH2Br2 (Dibromomethane)
HI (Hydrogen iodide)
NH4NO3 (Ammonium nitrate)
IF5 (Hydrogen cyanide)
OH2 (Hydroxide)
C2Cl2
NO+ (
SBr2
ICl4+
NO
CH3OH (Methanol)
SCl6
CH4O (Methanol)
ICl3 (Iodine
BrF5 (BROMINE PENTAFLUORIDE)
PCl5 (PHOSPHORUS PENTACHLORIDE)
CH2F2 (Difluoromethane)
SeH2 (Hydrogen
COS (Cobalt sulfide)
OF2 (Oxygen
H2SO4 (SULFURIC ACID)
H2CO (Formaldehyde)
NF3 (NITROGEN TRIFLUORIDE)
C2H2Br2 (Acetylene
TeF4
SCN
CLO3- (Chlorate)
ICl5
urea
SO2Cl2 (Sulfuryl chloride)
H2Se (Hydrogen
NH2
XeO3
SbF3
CaCl2 (CALCIUM CHLORIDE)
AsF3 (ARSENIC TRIFLUORIDE)
C2H2 (Ethyne)
Cl2O
IF3 (Iodine
SH2
SCl4
CO (Carbon monoxide)
H3O
HNO3 (NITRIC ACID)
N2H2
NBr3
So3 2-
CH3COOH (acetic acid)
salt
SeO2
CCl2F2
N2H4
C2H5OH
C2H6O (Ethanol-d6)
SOCl2
H3O+ (Hydronium)
CHF3 (Fluoroform)
NI3 (Nitrogen triiodide)
NaCl (sodium chloride)
AsH3 (Arsine)
NH2Cl
OCS (Carbonyl sulfide)
SiCl2F2
glucose
CH3
N2O
PoCl3 (PHOSPHORUS OXYCHLORIDE)
MgCl2
vinegar
IOF5
phosphate
CHBr3 (Bromoform)
PBr3 (PHOSPHORUS TRIBROMIDE)
SF2 (Sulfur
NH3 (ammonia)
SO2 (sulfur dioxide)
CH2Cl2 (DICHLOROMETHANE)
SF4
H2S (hydrogen sulfide)
CHCl3 (CHLOROFORM)
PCl3 (PHOSPHORUS TRICHLORIDE)
SCl2 (Sulfur
PH3 (Phosphine)
CH2O (Formaldehyde)
HF (HYDROFLUORIC ACID)
NCl3 (Nitrogen
PF3 (Phosphorus
NO3- (nitrate)
NO2 (Nitrogen dioxide)
H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide)
CH3Br (Bromomethane)
O3 (OZONE)
CH3CL (Chloromethane)
ammonia
OH- (Hydroxide)
NO2- COCl2 (Cobalt
glycerol
oh
chloroform
ether
no3
CLF5 methylene chloride
CH3SH
Na2SO4
CaCO3
1-
C4H10
libr
cabr2 (Calcium bromide)
CH3CN (ACETONITRILE)
CH3CH2CH2OH
C6H12O6
LiNO3 (Lithium nitrate)
MgO
SeOBr2
clo3
c3h7oh
glycerine
bri5
BrO2
CF3Cl
BF2Cl
IBr
GaCl3
KMnO4 (POTASSIUM PERMANGANATE)
Na2S (sodium sulfide)
KOH (POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE)
HCOOH
carbohydrates
ClO4
Cl2CO
clo2-
H2SO3 (Sulfurous acid)
ethyne
NO2F
CCL3F (Fluorotrichloromethane)
ammonium
ibr3
fluoromethane
C2H5Cl TeCl4
2-
starch
ch2cl
XeOF4
SnCl2
SCO (Carbonyl sulfide)
SbBr3
H2CS
HC2H3O2
Propanol
1-
bro3-
ch3ch2ch2ch3
CF2Br2
aniline
CF
phenol
clo2
CH2S
ch3cho
glass
SH
COH2
SOF4
DNA
CH3CH2NH2
Malonic Acid
SeCl4
ozone
c3h6o
formaldehyde
po3 3
difluoromethane
aspirin
CHCl2
HCl
nitrate
SCl
if4+
Molecules non polar
SiF4 (Silicon
CH3CH3 (Ethane)
N2 (Nitrogen)
CO3 2- (Carbonate)
XeO4 (Xenon
KNO3 (Potassium nitrate)
CH3I (Methyl iodide)
CBr4 (Carbon
AlCl3 (Aluminum
C6H6 (benzene)
NH4Br
C2H4Cl2 (
ligroin
SO4 2- (Sulfate)
C2H4
SF6 (Sulfur hexafluoride)
BH3 (Borane)
C2F2 (Ethyne)
C6H14 (HEXANE)
PO4 3- (phosphate)
GeH4 (Germane)
PBr5 (Phosphorus pentabromide)
NH4 (ammonium)
wax
CI4 (Tetraiodomethane)
bbr3 (BORON TRIBROMIDE)
H2 (Hydrogen)
IF4-
BeF2 (Beryllium
I2 (Iodine)
GaH3 (Gallane)
SeBr4 (Selenium
KrF4
SiBr4
C2H6 (Ethane)
O2 (Oxygen)
biphenyl
PO4 3
P4 (Phosphorus
SO4 2-
naphthalene
XeCl2
BrCl5
SeF6
SeO3
SiH4 (
AsF5 (Arsenic pentafluoride)
BeH2 (Beryllium
SiO2
KrF2
CH2
cholesterol
F2 (Fluorine)
pentane
ClF2
C3H8
Propane
cyclohexane
toluene
SiCl4 (Tetrachlorosilane)
chlorine
PF5 (Pentafluorophosphorane)
BrCl
CO2 (carbon dioxide)
CCl4 (CARBON TETRACHLORIDE)
XeF2
CS2 (CARBON DISULFIDE)
SO3 (SULFUR TRIOXIDE)
XeF4 (Xenon
BCl3 (BORON TRICHLORIDE)
BeCl2 (Beryllium
CF4 (CARBON TETRAFLUORIDE)
Cl2 (Chlorine)
Br2 (Bromine)
Hexane
i3-
carbon disulfide
methane
glycine
benzophenone
oxygen
AlF3 (Aluminum fluoride)
C8H18 (octane)
C2Cl4
PF6-
XeCl4
SbF5 (ANTIMONY PENTAFLUORIDE)
CH3CH2CH3
C5H12 (PENTANE)
silane
s8
BF4 BF4-
SeCl6
BeBr2
BeI2
CSe2
Pcl4
C3H6
AlH3 (Aluminum
TeO3 (Tellurium
AsCl5
octane
ClF4 plus
acids
kerosene
acetylene
C-C
ethane
CCl
Cl4
cbr
sulfate
butter
triglycerides
grease
silicon tetrafluoride
nitrogen
ICl2-
HE
CS
sis2
CH4
Ionic
NaBr
KCl
NaF
NaNO3
cao
MgF2
Resources
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chemical_polarity
http://www.school-for-champions.com/chemistry/polar_molecules.htm#.WZIGddJJbcc
reference.com
www.quora.com
answers.yahoo.com
youtube.com
google.com
https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
If the answer is wrong, please
Question = Is vitamin e polar or nonpolar
Answer = vitamin e is Nonpolar
EmoticonEmoticon